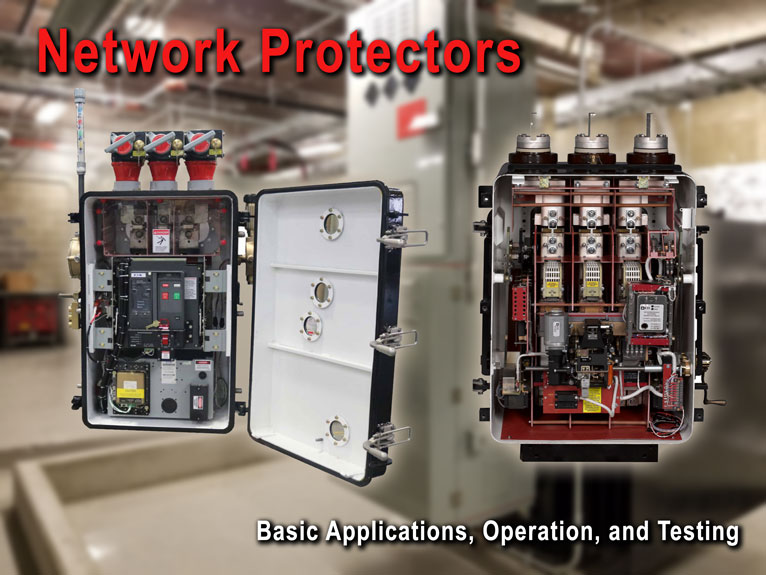
This guide covers network protector basic operation and maintenance procedures. Photo: TestGuy.
Network systems are commonly used in hospitals, high rise office buildings, and institutional facilities where a high degree of service reliability is required. In the network system arrangement, several utility services are paralleled at the transformer secondaries, creating a system that is dependable and versatile.
Distribution networks often utilize two or more transformers supplied from different high voltage feeders. The transformers are connected through network protectors to a common collector bar and the load served by cables or busses off the collector bus.
The most important elements of an a-c network power system are the network transformer and the network protector. These devices provide for automatic operation to reliably serve loads, isolate faults, and distribute power uniformly across the multiple primary circuits.

This guide provides a basic overview of the theory and procedures involved with infrared scanning electrical distribution systems. Photo: TestGuy
It's well known that the heat produced from high electrical resistance typically precedes electrical failures. For this reason, infrared scans are an essential measure for troubleshooting, diagnostics, and preventive maintenance in electrical power distribution applications.
Thermal imagers are most commonly used for inspecting the integrity of electrical systems because test procedures are non-contact and can be performed quickly with equipment in service. Comparing the thermal signature of a normally operating piece of equipment to the one being evaluated for abnormal conditions offers an excellent means of troubleshooting.

This guide provides a comprehensive overview of inspection and test procedures for protective relays in electrical power systems. Photo: TestGuy.
Protective relays are used extensively across the power system to remove any element from service that suffers a short circuit, starts to operate abnormally or poses a risk to the operation of the system. The relaying equipment is aided in this task by instrument transformers that sense power conditions and circuit breakers that are capable of disconnecting the faulty element when called upon by the relaying equipment.
Due to their critical role in the power system, protective relays should be acceptance tested prior to being placed in service and periodically thereafter to ensure reliable performance. In a normal industrial application, periodic testing should be done at least every 2 years in accordance with NFPA 70B 2016.

Surge arresters are voltage limiting devices used to protect electrical insulation from voltage spikes in a power system.
Similar to how a fuse functions to protect an electrical system from damage due to overcurrent conditions, the job of a surge arrester is to protect the system from damage due to overvoltage conditions.
Electrical test technicians are responsible for assuring that electrical power systems are in proper working order and are ready to be energized. Periodic tests on equipment already in service help prolong service life and indicate whether corrective maintenance or replacement is necessary.
Testing electrical equipment in the field is the best way to assure that it will perform its design functions safely and adequately. Hiring a certified third-party testing organization assures the equipment owner that all tests will be performed objectively, independent of the manufacturer, according to specifications, using calibrated instruments and personnel qualified for the task.

This guide provides a general overview of inspection and test procedures for simple residual and zero-sequence ground fault protection systems. Photo: TestGuy.
A ground fault is a type of electrical fault or short circuit condition that results from any unintentional connection between an ungrounded conductor of an electrical circuit and the normally non–current-carrying conductors, metallic enclosures, metallic raceways, metallic equipment, or earth.

This article provides an overview of some commonly used maintenance and diagnostic techniques that are commercially available for performing tests in the field on medium- and high-voltage power cables. Photo: TestGuy.
Field testing of medium- and high-voltage cables may performed for various reasons, such as acceptance after installation, charting the gradual deterioration of insulation over time, verification of splices and joints, and for special repairs. This assessment applies to both the cable itself, as well as the associated accessories (splices and terminations) — referred to as the "cable system."
Sharpen your skills with our collection of quizzes on electrical safety, maintenance & testing of electrical equipment and industry standards.
Tech Quiz Study Guide